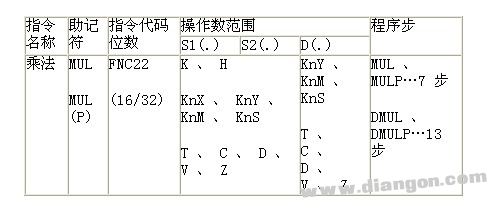
The mnemonic, instruction code, operand, and program steps of the instruction are shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Elements of the multiplication instruction
The MUL multiply instruction multiplies the binary number in the specified source component and sends the result to the specified target component. The instructions for using the MUL multiply instruction are shown in Figure 3. It is divided into 16 and 32 bits.
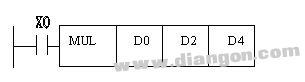
Figure 3 multiplication instructions instructions
When it is a 16-bit operation, when the execution condition X0 is turned from OFF to ON, [D0]x[D2]→[D5, D4]. The source operand is 16 bits and the destination operand is 32 bits. When [D0]=8, [D2]=9, [D5, D4]=72. The highest bit is the sign bit, 0 is positive and 1 is negative.
When it is a 32-bit operation, when the execution condition X0 is turned from OFF to ON, [D1, D0] x [D3, D2] → [D7, D6, D5, D4]. The source operand is 32 bits and the destination operand is 64 bits. When [D1, D0] = 238, [D3, D2] = 189, [D7, D6, D5, D4] = 44982, the most significant bit is the sign bit, 0 is positive, and 1 is negative.
If the bit combination component is used for the target operand, the value of K is limited to the result of the lower 32 bits, and the result of the upper 32 bits cannot be obtained. At this point, the data should be moved to the word component for calculation.
When using word components, it is also impossible to monitor 64-bit data, only by monitoring the upper 32 bits and the lower 32 bits. V, Z cannot be used for the [D] target component.
Replaceable Atomizer,Atomizer Replacement Bottle,Replaceable Atomizer On Vape Pen,Replacement Atomizer Set
Lensen Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.lensenvape.com