At present, in terms of audio signal processing in the excitation mode, there are an auditory exciter (AuralExciter), an excitation processing software, and an excitation circuit. Among them, professional auditory actuators are more suitable for EFP.
The harmonic signal excited by the auditory exciter is designed by simulation, which can be compared to the artificial reverberation to simulate the acoustic characteristics of the hall. Therefore, the generation of such artificial harmonics should not be simply regarded as the "inaccuracy" of the original signal and equivalent to distortion. The design purpose of the exciter is to restore the harmonic components lost in the audio signal, effectively expand the high-frequency bandwidth and improve the signal-to-noise ratio, thereby improving the clarity and expressiveness of sound restoration. Moreover, the levels of these harmonics are very low and have little effect on the power of the signal. Because the exciter has the above advantages, using it to process the signal can improve the sound quality.
In practice, we use AphexAuralExciter-â…¢-250 (referred to as Ax-â…¢-250) professional auditory exciter. Ax-â…¢-250 is a dual-channel processor, and each channel includes the same two audio paths, namely the main signal path (MainPath) and the side-chain excited signal path (SidechainPath). The main path sends the audio signal from the input stage directly to the output stage, basically without any processing; the side chain path contains all the "heart" circuits of the exciter. The two audio signals are mixed at the addition circuit level, and the mixing ratio is controlled by the Mix function. Ax-â…¢-250 has strong audio processing ability, and can effectively eliminate noise and distortion.
2. Control parametersThe main control parameters of the exciter are threshold, tuning point, harmonic amount, timbre and mixing ratio, etc., and they produce the high frequency harmonics to be restored in conjunction with each other. The main controls of Ax-â…¢-250 are:
(1) Noise reduction threshold (NRThreshold). The threshold setting range provided by this control is -60 ~ + 30dB, the purpose is to keep the noise level outside the excitation processing circuit and perform noise reduction.
(2) Tune point. This control sets the frequency of the rising edge of the second-order high-pass filter in the side-chain path and establishes the working frequency band of the excitation. The frequency control range is 700 Hz to 7 kHz.
(3) Peaking (Peaking). This control provides a buffering effect for the tuning point. When the control amount reaches the maximum from the minimum, the pre-emphasis of the tuning point frequency gradually increases. At the same time, before the pre-emphasis of the tuning point, there will be a small notch, which will deepen with the increase of the peaking control.
(4) Zero value compensation (NullFill). The function of the zero-value compensation control is to adjust a band-pass signal, which is added to the high-pass signal in the side chain path to compensate for "phase loss".
There is a certain delay in the signal in the side chain path, which will cause distortion of the transient waveform and make the sound louder. At the same time, a small notch will appear near the tuning point on the output equalization curve. This notch will de-emphasize the frequency near the tuning point, making the higher frequency band signal heavier. This effect is often needed. But sometimes in order to compensate for the phase loss, the zero value compensation control is used to de-emphasize, thereby improving the expressiveness and realism of the sound.
(5) Harmonic quantity (Harmonic). Tuning control is used to adjust the amount of harmonic generation. Harmonics are generated by VCA modulation processing in the sidechain path, and it does not affect the signal level in the sidechain path. The harmonic components generated by the internal harmonic generator are based on a complex set of simulation operations, and the transient and steady-state sound quality and the corresponding original signal amplitude must be considered.
If the amount of control is increased, the harmonic content will be increased according to the odd and even harmonic proportion of timbre control. Moreover, the generated harmonics are not harmonic distortion, because they are intelligently generated and form a power envelope, so that the final sound quality is improved rather than deteriorated.
(6) Timbre (TImbre). Tone control is used to set the type and arrangement of harmonics, that is, the ratio of odd and even harmonics. Sounds with even harmonics sound softer, and sounds with odd harmonics sound harder.
(7) Mixing ratio (Mix). The function of the mixing ratio control is to mix the signal with enhanced excitation into the original signal, and the control range is from 0dB (that is, zero gain) to + 14dB (indicating that the signal above the threshold is boosted by 14dB).
In addition, Ax-â…¢-250 also provides a single-select side chain path (Solo) function.
3. System accessThe access of the exciter generally has two forms: series connection (In-Line) and side chain (Sidechain). as shown in picture 2. In most cases, the serial connection method is used to connect the exciter between two devices. When using the side-chain connection method, use the Solo function to disconnect the audio signal of the main path, only let the pure excitation signal enter the mixing console, and mix the original signal and the pure excitation effect signal on the mixer. This is very important. This connection is equivalent to moving the Mixer control of the exciter to the mixer, and the mixer itself is a mixing console, so it is more convenient and flexible to control, which is conducive to accurately tracking and controlling the auditory effect.
In practice, a dual channel of an Ax-â…¢-250 is used to simultaneously process multiple audio signals in the EFP. Connect the exciter to the audio system as shown in Figure 3. Among them, CH1 channel is allocated to vocal use, and CH2 channel is allocated to music use. At this time, the auditory exciter is in a form of side-linking. The original flow of the program signal has not changed. The signal is transmitted and mixed according to the original channel; at the same time, it provides two pure excitation effects. These harmonics are sent to the source of the exciter The signal is closely related to music and dynamics. The original signal and pure excitation signal are only mixed and mixed on the mixer.
The specific method is to use one set of control parameters of CH1 to process FM audio or vocals from wireless microphones, and another set of control parameters of CH2 to process music or other sounds whose sound quality needs to be improved (such as electro-acoustic bands, etc.). Because the sound quality of these program sources is inconsistent, it is necessary to determine the amount of stimulus addition according to the situation of the material and track and adjust the mixing ratio.
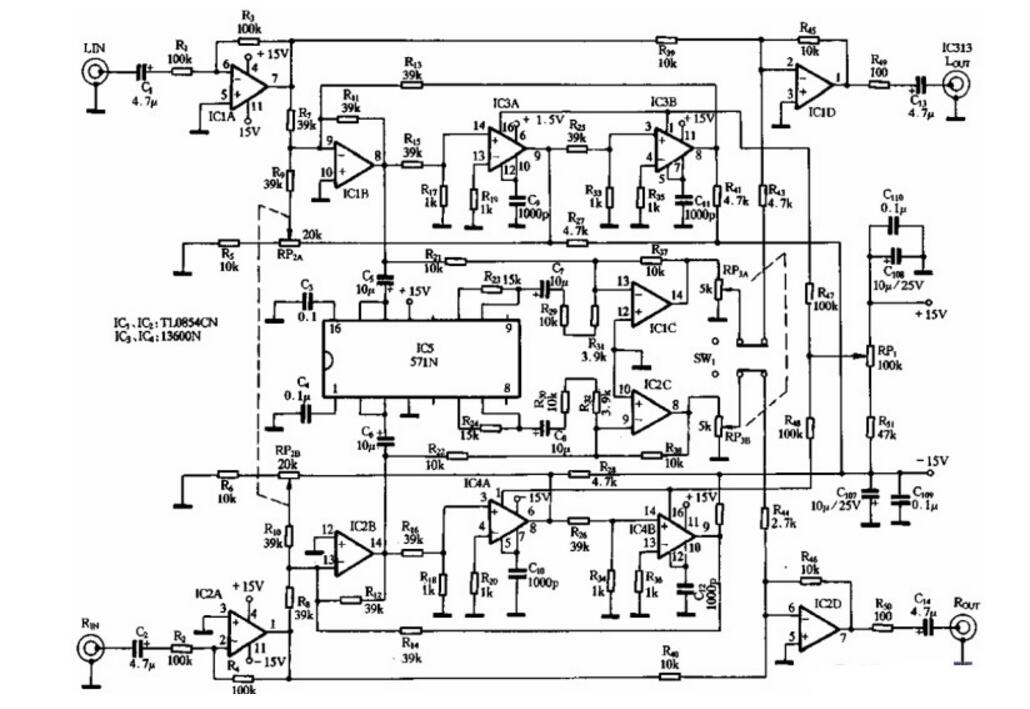
The schematic circuit diagram of the exciterAbout the principle circuit diagram of the sound exciter. Among them, the audio signal is input to the inverting buffer iqA through cr and RI, and its 7-pin output signal is divided into two channels. All the way through the ‰ input directly into the synthetic output stage composed of iqD. The other channel is a voltage-controlled state variable high-pass filter composed of iqB, IC3A, and IC3B via R7. Its corner frequency is determined by R15, Rzs, q, cll, and Ic internal voltage-controlled variable transconductance elements, and passed through the potentiometer The adjustment of RPi makes the turning frequency change between 2 ~ 8kHZ, and the signal below the turning frequency is attenuated by l2dB octave. Adjusting RPZA can change the negative feedback of IC3A9's band-pass output to the inverting input of IClB9, thus changing the Q value of the filter, because Q = (Wei ‰ + Rg) / R ll, the adjustment range of the value is l- 0 ~ 1, 50IC3 is a dual operational transconductance amplifier, model 13600. ICIB8 pin is the output terminal of the voltage-controlled state variable high-pass filter. The actual circuit is shown below.
(1) Determination of the incentive object: What sound source should we use the exciter to deal with? There must be a clear concept, whether to deal with music or vocals alone? Or both? Generally speaking, the effect of the exciter on the human voice is more obvious; the effect of processing the individual music is also obvious; but when the mixture of music and human voice is processed, the effect is relatively less obvious.
(2) The connection of the exciter: The connection of the exciter is basically connected in series to the signal channel that needs to be excited in the sound system like the peripheral equipment such as an equalizer. When performing excitation processing on different targets, the connection method of the exciter is also different. For example, in a mixer, the 1-2 group is the human voice. If you want to excite the human voice, you must insert the exciter. / The plug-in interface is connected to the 1-2 group channel of the mixer; if the band of the 3-4 group also needs to be excited, then an exciter must be added to connect to the mixer using the plug-in / out interface 3-4 groups; if you want to perform comprehensive processing, then just connect an exciter in series in the main channel of the mixer. Of course, the exciter can also send a signal from AUX like an effect device, and then return to the mixer, so that you can adjust which channels need to be excited and how hard they need to be processed. This is actually more flexible. In short, the specific connection of the exciter should be used flexibly according to the situation!
(3) Adjustment method of the exciter:
Audio exciters are not currently used in audio systems too much, mainly because the engineering companies have not paid enough attention to the exciters, plus there are not many high-quality exciters in the industry in recent years, so now I think that the exciter is a bit "edge" melted. At present, the more famous actuators in the industry are: Aphex, BBE, BEHRINGER, etc. They have their own characteristics, but the general functions, principles and parameters are basically the same. Here I will not introduce a specific actuator specifically, just briefly Overall aspect:
Exciter function key introduction:1. IN / OUT plus or without exciter effect selection: This key is mainly used for effect comparison during adjustment.
2. TUNE (tuning) exciter signal fundamental frequency adjustment: mainly used to select the frequency that needs excitation processing.
3. MIX (mixed) harmonic output control: mainly used to control the magnitude of excitation intensity.
4. HIGH / NORMAL: HIGH is suitable for excitation processing of single sound sources such as vocals and musical instruments; NORMAL is suitable for excitation processing of music with a wide range of sounds such as overall music.
The above four function keys are called: the auditory exciter part, which is mainly used to adjust the penetration of high frequency harmonics and sound.
5. OVERHANG (bass hold time): This is mainly for adjusting the bass length.
6. GIRTH (low volume): bass intensity adjustment.
The above two function keys are unique to the exciter with low frequency expansion function, and can adjust the bass tone.
Exciter adjustment method:1. Put IN / OUT in "IN": At this time, the corresponding indicator lights up, so that the exciter will enter the working state.
2. TUNE placed at 12 o'clock: This knob should be adjusted flexibly according to the need of excitation frequency.
3. HIGH / NORMAL is placed in the required position: NORMAL for comprehensive treatment, and HIGH for other treatments.
4. MIX (harmonic amount) and GIRTH (low volume): both are placed at the minimum position when starting the adjustment.
5. Raise MIX until you hear the flanger sound (the sound becomes brighter): pay attention to listening, this sound is not particularly obvious.
6. Adjust TUNE to improve the timbre or penetration of the sound: pay attention to distinguish the timbre. When adjusting, you can use music and microphone to adjust in turn, generally to the 11-14 o'clock position similar to the clock.
7. Repeat the adjustment of MIX until the harmonic effect is satisfied: generally adjust to the 13-15 o'clock position of a similar clock.

1. When connecting the exciter in the sound system, you must pay attention to the flow of the signal. If in a mixer, we are going to use an exciter to comprehensively process music and vocals, then you can use the main An exciter is connected in series behind the channel output signal; if only the 3-4 groups in the mixer are processed, then use the 3-4 groups: the plug-in / out interface is connected to an exciter, so 3- After the 4 groups are stimulated, they are sent through the main channel signal of the mixer; of course, if the sound of the 3-4 group is not sent through the main channel of the mixer at this time, it is directly through the 3-4 group itself The signal output port is directly sent out, then we can not use: insert / plug out method to connect the exciter, you can directly connect an exciter in series after the output signal of 3-4 groups. It seems simple. If the connection is wrong, the whole effect will change. Of course, to fully understand the connection and use of the actuator, it is up to everyone to study more.
2. If there is a level selection on the rear panel of the exciter, it is generally +4 and -10dB or +4 and -20dB. Then we must choose it at the + 4dB position, so as to ensure the matching of the signal level.
3. When using IN / OUT to compare the effect of sound with and without excitation, many sound engineers cannot distinguish the subtle differences in sound, because the sound emitted from the speaker rarely radiates directly into the ear of the sound engineer. It is difficult to accurately distinguish between the sound effects with and without excitation. In fact, there is a simple way: if we connect the output signal of the left channel of the exciter to the first channel of the mixer, but pay attention to that the volume fader of this channel should be turned off. Then we can put on headphones to monitor the sound of the first channel separately. At this time, we have a high ability to distinguish the sound effects with and without excitation, and then take off the headphones to adjust the right channel of the exciter. Then distinguish the effect from the on-site speakers, so that the combination of the two can quickly bring up a perfect effect.
4. In music-based audio systems, such as discotheque, the exciter can be used to make larger adjustments. The bass volume and bass time can be adjusted to satisfaction, and the mid-treble can also be greatly Adjust to achieve strong penetration. Because of the turbulent flow of people in these places, the sound absorption is very strong, and the background noise is large, so it is very necessary to use an exciter to adjust.
5. In the audio system mainly based on human voice, such as: in the singing stage, use exciter to adjust carefully, bass volume and bass time must be adjusted repeatedly, too much bass affects the clarity of human voice, bass Too little sound seems too thin and not full, so adjust to the right. The adjustment of the midrange and treble actually needs to be flexibly adjusted according to different vocals. Because the pitch frequencies of male singers and female singers are different, the harmonics (overtones) that need to be processed by the exciter will of course also be different. Therefore, pay attention to this difference when making adjustments.
6. Some sound fields have too many smooth reflection areas, so the reflection of the treble is very strong, and the sound quality is also very noisy. If you add an exciter to increase the "penetration", it will undoubtedly add to the snow, and the treble will become more harsh and noisy. Therefore, a good sound field is very important, and the exciter cannot be used in any place.
8. Raise the OVERTHANG and adjust its indicator to flash: generally adjust to the 11-14 o'clock position similar to a clock. The bass time is too short without fullness, and too long is easy to be cloudy. Be careful to adjust it.
9. Raise GIRTH and adjust OVERTHANG at the same time until the bass effect is satisfied: generally adjust to the 10-13 o'clock position similar to a clock.
In the adjustment process, you can use IN / OUT to compare the sound effect with and without excitation, and adjust it repeatedly until the treble is bright and clear, the bass is full and flexible, and the hardness is suitable. Of course, there are various types of exciters now, and their functions and adjustment methods are different. We can only adjust each audio device by learning more, watching more, and listening more.
Passive Line Array,Line Array Passive Speakers,Passive Line Array Speakers,Passive Array Speakers
NINGBO LOUD&CLEAR ELECTRONICS CO.,LIMITED , https://www.loudclearaudio.com