High-power LEDs have developed very rapidly, and have become mainstream lighting sources in various lighting applications. More and more friends are familiar with and familiar with LED driver power. It is no exaggeration to say that the LED driver power supply will directly determine the reliability and life of the LED lamp. Today, we will simply analyze an LED driver circuit for everyone to learn.
First, start with a complete LED driver circuit schematic. The picture used in this article is obtained from the Internet and does not represent a specific product. It is mainly intended to share the current principle of constant current driving power supply from this picture, and share with you the understanding of Daniel. Hope it could help everyone. Then this article only does qualitative analysis, only the process of the signal, the parameter quantity of the specific voltage and current is not discussed here. As shown in Figure 1 of an LED driver circuit schematic, this is an AC/DC input mode LED driver circuit, using electroless capacitors. It is a typical LED driver circuit.
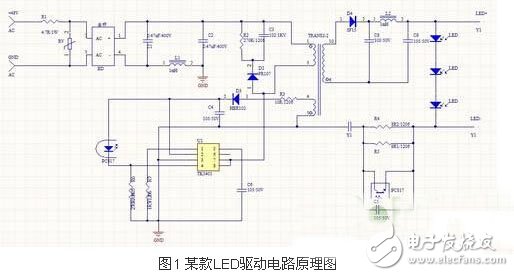
Second, the principle analysis: In order to facilitate the analysis, divide Figure 1 into several parts
1: Input overvoltage protection - mainly due to lightning or city surges)
Input overvoltage protection circuit is shown in Figure 2:
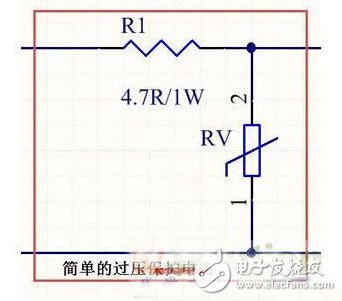
Figure 2 Input overvoltage protection circuit
If the DC voltage comes from both ends of "+48V, GNG" and passes through the resistor of R1, the function of this resistor is current limiting. If a short circuit occurs in the following line, the current flowing through R1 will increase, and then the voltage will be increased at both ends. The drop is followed by an increase. When it exceeds 1W, it will be automatically disconnected, and the resistance will increase to infinity, so that the protection input circuit +48V will not be affected by the load.) After the current limit, the rectifier bridge is entered. R1 and RV constitute a simple overvoltage. Protection circuit, RV is a pressure sensitive component, which is made of semiconductor material with nonlinearity. Its volt-ampere characteristics are similar to those of Zener diodes. Normally, it has a high impedance state, and there is little current flowing. When the voltage is high. At a certain time (mainly refers to spikes, such as high pulse bursting through the mains when thunder), the pressure sensitive RV will appear short-circuit state, directly intercept the entire input total current, so that the latter circuit stops working, this Since all current will flow through R1 and RV, since R1 has only 1W of power, it can be opened instantaneously, thus protecting the entire circuit from damage.
2. Rectifier filter circuit: When the AC input is AC, the bridge rectifier is the most commonly used circuit for rectifying by using the single-conductivity of the diode, and converts the alternating current into direct current. When the DC DC (+48V) voltage directly enters the rectifier bridge BD, it outputs a DC voltage that is positive and negative. If the +48V power supply is also DC, the function of the rectifier bridge is to protect the input from polarity. No matter whether the input is up, down, or negative, the drive power will not be damaged. The filter is filtered by C1\C2\L1. Figure 3 is an LCÎ filter circuit designed to smooth the rectified voltage waveform with DC power.
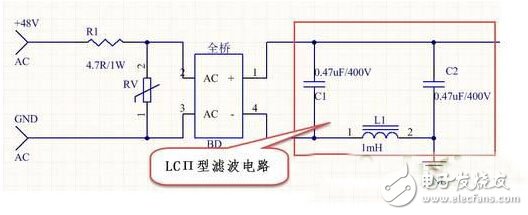
Figure 3 LCÎ type filter circuit
High Frequency Transformer,High Voltage High Frequency Transformer,High Requency Transformer Used For Machine,High Power High Frequency Transformer
Guang Er Zhong(Zhaoqing)Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.poweradapter.com.cn